TypeScript vs JavaScript: Which One Is Better?
In modern web development, few debates are as persistent as TypeScript vs JavaScript, especially for businesses and developers deciding on the right technology stack. While JavaScript has long been the backbone of the web, TypeScript has rapidly gained popularity for its structure, scalability, and enterprise readiness. The question of TypeScript or JavaScript is no longer just technicality directly affects application performance, maintainability, and long-term development costs. This article provides a clear, human-centric comparison to help you determine which option is better for your specific needs.
Understanding JavaScript: The Foundation of the Web
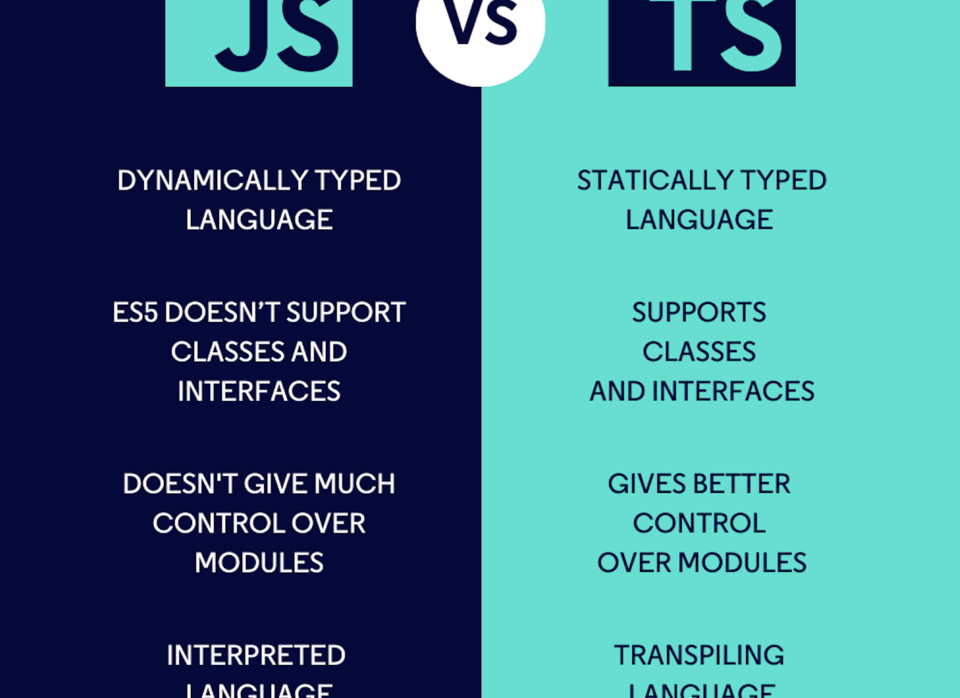
JavaScript is a dynamic, interpreted programming language that runs natively in all modern browsers. For decades, it has powered interactive websites, web applications, and even server-side solutions through environments like Node.js. When evaluating TypeScript or JavaScript, it is important to recognize JavaScript’s flexibility and accessibility, which make it ideal for beginners and rapid prototyping.
However, JavaScript’s dynamic typing can sometimes introduce runtime errors that are difficult to detect during development. While this freedom is powerful, it can also become a liability in large-scale applications where maintaining consistency is critical.
What TypeScript Brings to the Table
TypeScript is essentially a superset of JavaScript, meaning it builds on JavaScript while adding optional static typing and advanced tooling. In the debate of TypeScript or JavaScript, TypeScript often stands out for its ability to catch errors at compile time rather than at runtime.
By enforcing type definitions, TypeScript improves code clarity and predictability, especially in complex projects with multiple developers. This structured approach makes it easier to refactor code, scale applications, and maintain long-term stability without sacrificing JavaScript compatibility.
Learning Curve and Developer Experience
From a learning perspective, TypeScript or JavaScript can lead to very different onboarding experiences. JavaScript is generally easier for beginners due to its minimal syntax requirements and immediate feedback in the browser. New developers can see results quickly, which encourages experimentation.
TypeScript, on the other hand, requires a deeper understanding of types, interfaces, and compilation processes. While this can initially slow down development, many teams find that the improved developer experience, such as better autocomplete, error detection, and documentation, quickly outweighs the learning curve.
Performance and Execution
A common misconception in the TypeScript or JavaScript discussion is that one performs faster than the other at runtime. In reality, TypeScript compiles down to JavaScript before execution, meaning browser and server performance is effectively the same.
The real performance difference lies in development efficiency. TypeScript’s early error detection can significantly reduce debugging time and production issues, leading to more stable applications and lower long-term costs for businesses.
Scalability and Maintainability
When applications grow, maintainability becomes a critical factor in choosing TypeScript or JavaScript. JavaScript works well for small projects, but as codebases expand, the lack of enforced structure can result in technical debt.
TypeScript excels in large-scale systems by providing clear contracts between components. This makes collaboration easier, especially in distributed teams, and ensures that updates or new features do not unintentionally break existing functionality.
Ecosystem and Tooling Support
Both technologies benefit from a rich ecosystem of libraries and frameworks. In the TypeScript or JavaScript comparison, it is worth noting that most modern frameworks, such as Angular, React, and Vue, either support or strongly encourage TypeScript usage.
TypeScript also integrates seamlessly with modern IDEs, offering superior tooling, intelligent code completion, and automated refactoring. These features enhance productivity and reduce human error, particularly in professional development environments.
Business Considerations and Cost Implications
From a business standpoint, the choice between TypeScript or JavaScript should align with project goals, timelines, and budgets. JavaScript may reduce initial development costs due to faster setup and a larger pool of entry-level developers.
However, TypeScript often delivers a stronger return on investment for long-term projects. Fewer production bugs, easier onboarding for new developers, and improved maintainability can significantly reduce operational costs over time.
The Role of AI in Modern Development
As AI-driven development tools become more sophisticated, the TypeScript or JavaScript decision takes on new relevance. AI-assisted code generation, automated testing, and intelligent debugging benefit greatly from structured, strongly typed codebases. Could AI-powered development tools become even more accurate and reliable when working with TypeScript’s explicit type definitions rather than JavaScript’s flexible syntax?
Conclusion: Which One Should You Choose?
Ultimately, the choice between TypeScript or JavaScript depends on your project’s scale, complexity, and long-term objectives. JavaScript remains an excellent option for simple applications, rapid prototyping, and learning environments. TypeScript, however, is better suited for enterprise-level solutions, complex systems, and teams prioritizing scalability and maintainability.
For organizations seeking expert guidance in selecting and implementing the right technology stack, clients should reach out to Lead Web Praxis for professional consultation, development services, and future-ready digital solutions.